Can Gum Disease Cause Tooth Loss?
By :
Affordable Dentist | April 02, 2024
Your smile is one of your greatest assets. It radiates confidence, makes a positive first impression, and allows you to enjoy your favorite foods. But a healthy smile doesn't happen by chance. It requires consistent care and vigilance against threats like gum disease, a leading cause of tooth loss in adults. This blog post dives deep into the connection between gum disease and tooth loss. We'll explore how this infection silently wreaks havoc on your oral health, the warning signs to watch out for, and most importantly, how to prevent it from stealing your smile.
Understanding Gum Disease: From Gingivitis to Periodontitis
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an infection that attacks the tissues and bones that support your teeth. It's a progressive condition, meaning it worsens over time if left untreated. There are two main stages of gum disease:
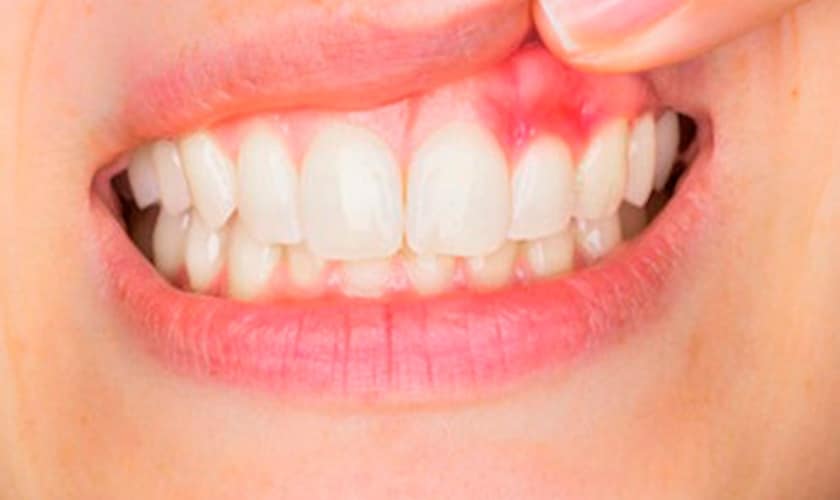
Gingivitis: This is the early stage of gum disease. It's caused by a buildup of plaque, a sticky film teeming with bacteria, at the gumline. Gingivitis symptoms include red, inflamed gums that bleed easily during brushing or flossing. The good news is that gingivitis is reversible with proper oral hygiene practices and professional dental cleanings.
Periodontitis: If gingivitis goes untreated, it can advance to periodontitis. This more severe stage involves the breakdown of the bone and connective tissues that hold your teeth in place. Periodontitis symptoms include persistent bad breath, receding gums, loose teeth, and pus seeping from around the teeth. In its most advanced stages, periodontitis can lead to tooth loss.
How Does Gum Disease Cause Tooth Loss?
Healthy gums play a vital role in keeping your teeth strong and stable. They act like a secure socket, firmly ensconcing the root of your tooth in the jawbone. However, gum disease, if left unchecked, can dismantle this supportive system. As a result, it ultimately leads to tooth loss. Here's a closer look at this destructive process:
Invasion and Irritation
The culprit behind gum disease is the buildup of plaque, a sticky film teeming with bacteria. When plaque isn't removed through regular brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar (calculus), which clings stubbornly to the teeth. These bacteria irritate the gum tissue, causing inflammation and redness. This is the initial stage of gum disease, called gingivitis.
Infection Takes Root
If gingivitis remains untreated, the bacteria continue to multiply and invade deeper below the gum line. This triggers an immune response from the body, further inflaming and weakening the gum tissue. Pockets begin to form between the gums and teeth, creating ideal breeding grounds for even more harmful bacteria.
Breakdown of Support
As the infection progresses, it starts to break down the fibers and bone that anchor your teeth in place. These supportive structures are crucial for keeping your teeth firmly planted. With their foundation weakening, the pockets around the teeth deepen, exposing more root surfaces and making them even more susceptible to bacterial attack.
Loosening and Potential Loss
With the continued destruction of bone and tissue, the grip on your teeth loosens significantly. This can cause your teeth to become sensitive, especially when chewing, and may even lead to them shifting out of position. In severe cases, the weakened teeth can't stay anchored and eventually fall out.
Additional Complications
Beyond tooth loss, severe gum disease can negatively impact overall health. The bacteria in your mouth can enter the bloodstream and contribute to other health problems like heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
Don't Ignore the Warning Signs: Recognizing Gum Disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a serious infection that affects the tissues supporting your teeth. Early detection and treatment are crucial to prevent it from progressing and causing tooth loss. Here are some key signs to watch out for:
Changes in Gum Color and Texture: Healthy gums should be pink and firm. Look for redness, inflammation, or swelling, which can be signs of early gum disease.
Bleeding Gums: Brushing or flossing shouldn't cause your gums to bleed. If you notice even minor bleeding, it's a sign of irritation and potential infection.
Persistent Bad Breath (Halitosis): Although occasional bad breath is common, persistent bad breath that doesn't improve with brushing or mouthwash could indicate gum disease.
Receding Gums: Over time, gum disease can cause the gums to pull away from the teeth, making your teeth appear longer. This exposes the sensitive tooth root surface and increases the risk of infection.
Loose Teeth: In advanced stages, gum disease can loosen the grip of the tissues and bone around your teeth. This can lead to teeth feeling loose or wiggly.
Discomfort While Chewing: Pain or tenderness when chewing can be a sign of gum inflammation or damage to the underlying bone.
Pus Coming From Around the Teeth: Pus is a collection of white blood cells fighting infection. If you notice pus around your teeth, it indicates a gum infection that needs professional attention.
Effective Strategies to Prevent Gum Disease
Brush Twice a Day, Two Minutes Each: Consistency is key! Brushing twice a day, morning and night, disrupts plaque buildup, the sticky film harboring harmful bacteria. Aim for two minutes each time – set a timer or hum your favorite song twice to ensure thorough cleaning.
Soft Touch, Big Results: Choose a soft-bristled toothbrush. Harsh bristles can irritate your gums, potentially causing them to recede. Soft bristles effectively remove plaque without damaging delicate gum tissue.
Fluoride for the Win: Use toothpaste containing fluoride. Fluoride strengthens tooth enamel, making it more resistant to decay, which can contribute to gum problems. Look for the American Dental Association (ADA) seal of approval on your toothpaste.
Gumline Focus: Pay attention to the gumline! Gently angle your brush at a 45-degree angle where your gums meet your teeth, and brush in short strokes. This removes plaque buildup that can lead to gum inflammation.
Flossing Daily: Brushing alone can't reach everything. Flossing daily removes plaque and food particles from between your teeth, areas inaccessible to your toothbrush. This helps prevent plaque buildup and gum irritation in those hard-to-reach spaces.
Healthy Diet: What you eat plays a role in your oral health. Maintaining a healthy diet low in sugar and processed foods can help reduce the growth of bacteria in your mouth that contribute to gum disease. Choose fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources to nourish your body and promote gum health.
If gum disease is left untreated, it can indeed lead to tooth loss. It's crucial to prioritize oral hygiene and seek professional dental care to prevent the progression of gum disease. Regular dental check-ups, proper brushing and flossing techniques, and a healthy lifestyle can all contribute to maintaining healthy gums and teeth for a lifetime. Remember, early detection and intervention are key to preserving your smile and overall oral health.