Dental sealants are thin plastic coatings that are applied to the chewing surfaces of teeth. By filling and covering the microscopic grooves around the teeth, these tooth sealants prevent dental cavities and microbial build-up. Dental sealants are frequently placed on the backs of premolars and molars since chewing necessitates their use. The adult dental sealant forms a protective coating over the enamel by quickly bonding into the grooves and depressions of your teeth.
Who Should Have Dental Sealants Placed On Their Teeth?
Dental decay in the premolar and molar grooves and depressions is more common in children and teenagers. On one side, their susceptibility makes children perfect candidates for dental sealants treatment. Adult tooth sealants, on the other hand, are beneficial for older candidates without dental disease or fillings in their premolars and molars.
Children and teenagers should have dental sealants placed once their permanent premolars and molars have erupted. This aids in the protection of juvenile teeth during their cavity-prone years, which last from the ages of six to fourteen.
Children's and teenagers' diets, as well as their fondness for sweet foods, greatly enhance their chances of developing tooth decay and cavities. Dental sealants, on the other hand, give a long-lasting layer of protection for their premolars and molars. Children and teenagers who do not receive dental sealants are three times more likely to develop tooth cavities and decay, according to studies.
Dental sealant therapy for younger children may be recommended if an infant's teeth have deep grooves and depressions. The quality of a child's baby teeth is crucial because they determine how far apart permanent teeth should be spaced. We don't want these baby teeth to fall out too soon.
How Do Dental Sealants Work?
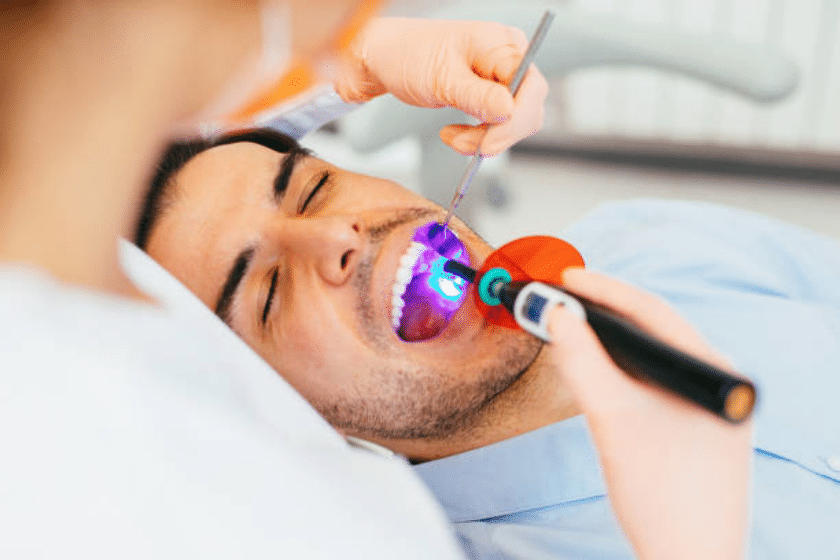
The application of an adult dental sealant is a reasonably painless and uncomplicated procedure. In a matter of minutes, your dentist will apply the sealant to each tooth. Applying a dental sealant entails the following steps:
- Dental sealants must be applied to teeth that have been thoroughly cleaned.
- Each tooth must be dried after cleaning by enveloping it in a ball of cotton wool or another absorbent substance.
- After that, the dentist applies an acidic solution to the chewing tooth's surface to prepare it for the dental sealant bonding procedure.
- The dentist rinses and dries your teeth to remove the acidic solution.
- Finally, the dentist places dental sealants on the chewing tooth's surface as well as all the way around the tooth enamel. The sealant hardens after adhering to each tooth. If necessary, a special curing light can be used to help solidify the sealant.
What Is the Expected Life Expectancy Of Dental Sealants?
Dental sealants endure a long period under normal circumstances. In most cases, dental sealants can protect your teeth from cavities and dental disease for a decade before they need to be replaced.
It's vital to remember that your dental sealants should be evaluated for chipping and wear at regular dental checkups. Because the teeth are no longer protected by their protective coverings when dental sealants peel off or are removed, they become vulnerable to dental cavities.
Dental Sealants: How Safe Are They?
Here's a quick rundown of
whether the benefits of dental sealants outweigh the hazards. When you Google "tooth sealants," you're likely to come across concerns about dental sealants' safety. As a plastic product, tooth sealants contain trace levels of Bisphenol A, better known as BPA. To put things in perspective and allay anxieties, this is comparable to the amount of plastic found in other everyday items like cups and bottles.
Despite the fact that dental sealants contain BPA, the amount in these tooth sealants is insignificant. The truth is that the amount of BPA in tooth sealants is well below the hazardous limit, making them completely safe.
To have a better knowledge of the amount of BPA released through dental sealants, the American Dental Association (ADA) conducted a study on 12 people who had dental sealants. The organization also wanted to know if this level of BPA was harmful to patients, and the research found that it was. Most adult dental sealants release about 0.09 ng of BPA into patients per day, which is much less than the EPA's daily exposure limit of 1 million ng. More BPA is found in cosmetics, foods, drinks, cash register receipts, and other products than in dental sealants.
The majority of BPA is exposed during the first several hours after tooth sealants are applied. While BPA exposure from dental sealants decreases over time, following these tips immediately after the procedure helps to considerably reduce BPA exposure:
- After the procedure, rinse your mouth for around 20 seconds with water. BPA exposure is reduced by around 68 percent as a result of this.
- Clean the affected tooth surface with a cotton swab. BPA exposure is reduced by roughly 87 percent as a result of this method.
- To reduce BPA exposure by roughly 95%, rub the dental sealant area with soft-grit pumice.
Make an appointment with My Affordable Dentist Near Me immediately for a safe and effective dental sealants process. We provide the
best dental care in Texas, United States. As your favorite Texas dentist, our goal is to offer everyone access to affordable, safe, and effective dental care.